Blockchain in supply chains is transforming how goods move from origin to consumer. This innovative technology offers a secure, transparent, and efficient way to manage every stage of the process, from raw materials to final delivery. Traditional systems often struggle with visibility and trust issues, but blockchain provides an immutable record of every transaction, creating a shared, verifiable truth across the entire supply chain.
By leveraging cryptography and distributed ledger technology, blockchain significantly enhances transparency, traceability, and security. This fosters trust among all stakeholders, including manufacturers, distributors, retailers, and consumers. The potential benefits include reduced costs, increased efficiency, and a more sustainable supply chain.
Introduction to Blockchain in Supply Chains
Blockchain technology is fundamentally changing how businesses operate, particularly in supply chains. It offers a secure, transparent, and efficient way to track goods and materials throughout the entire process, from origin to consumer. This innovative technology is revolutionizing industries by enhancing traceability, reducing fraud, and boosting overall supply chain resilience.Blockchain’s core principles are built around decentralization, immutability, and transparency.
These features enable secure and auditable records of transactions, eliminating the need for a central authority and reducing the risk of manipulation. This decentralized nature fundamentally differs from traditional centralized supply chain management systems, where a single entity controls data and processes.
Blockchain vs. Traditional Supply Chain Management
Traditional supply chain management systems often rely on disparate databases and manual processes. This can lead to inefficiencies, lack of transparency, and potential for errors. Blockchain, on the other hand, offers a unified, shared ledger accessible to all participants. This shared view of the supply chain fosters trust and accountability, significantly improving the overall system. Data integrity is inherently preserved due to the immutable nature of blockchain records.
Potential Benefits of Blockchain in Supply Chains
Implementing blockchain in supply chains offers a multitude of advantages. Enhanced transparency allows for real-time visibility into the movement of goods, enabling stakeholders to quickly identify and address potential issues. Improved traceability allows for complete product provenance tracking, providing consumers with detailed information about the product’s journey. Reduced fraud and counterfeiting is possible due to the immutability of the blockchain ledger, creating a more secure and trustworthy system.
Efficiency gains arise from automated processes and reduced paperwork.
Industries Utilizing Blockchain in Supply Chains
Several industries are already leveraging blockchain’s capabilities to optimize their supply chains. The food industry is one prominent example, using blockchain to track the origin and journey of food products, ensuring food safety and authenticity. Pharmaceutical companies utilize blockchain to maintain the integrity of medications, guaranteeing their quality and safety from manufacturing to consumption. The automotive industry leverages blockchain to manage vehicle parts, ensuring transparency and accountability throughout the supply chain.
Furthermore, the fashion industry employs blockchain to trace textiles, enabling ethical sourcing and preventing counterfeit goods.
Examples of Blockchain Applications in Supply Chains
Several real-world examples demonstrate the effectiveness of blockchain in supply chain management. Walmart’s use of blockchain to track food products demonstrates the potential to trace food origins and enhance transparency. Similarly, IBM’s Food Trust initiative shows the industry’s potential to combat food fraud. These examples illustrate how blockchain can create trust and accountability throughout the supply chain.
Enhancing Transparency and Traceability
Blockchain technology significantly enhances transparency and traceability in supply chains by creating a shared, immutable record of transactions and movements of goods. This distributed ledger system fosters trust and accountability throughout the chain, offering unprecedented visibility into the journey of products. The system’s inherent security and immutability make it ideal for verifying the authenticity and origin of goods, mitigating fraud, and improving efficiency.
Blockchain’s Impact on Supply Chain Transparency
Blockchain’s decentralized nature allows all participants in the supply chain to access and verify the same information about a product’s journey. This shared record eliminates the need for intermediaries to trust each other, promoting trust and cooperation. By recording every transaction and movement of a product, blockchain provides a complete audit trail. This level of transparency allows for real-time monitoring of the product’s location, handling, and any quality checks, improving overall efficiency.
Mechanisms for Tracking Goods
Blockchain’s distributed ledger technology facilitates the tracking of goods throughout the supply chain by recording each step of the process. Every transaction, from raw material sourcing to final delivery, is recorded as a unique block in the chain. This creates a permanent and tamper-proof record, ensuring that all parties have access to the same, accurate information. Smart contracts can automatically trigger actions based on predefined conditions, such as releasing payment upon reaching a certain location or notifying relevant parties of quality issues.
For instance, a shipment of pharmaceuticals could be tracked from the manufacturer’s facility to the retailer’s warehouse, with each step verified and timestamped on the blockchain.
Role of Digital Identities and Records
Digital identities play a crucial role in supply chain transparency, enabling authentication and verification of participants. Each actor in the supply chain, from farmers to retailers, can have a unique digital identity, verified and secured on the blockchain. This digital identity allows for secure authentication of goods and documents, preventing counterfeiting and fraud. Records related to quality control, certifications, and other relevant information can also be securely stored on the blockchain, providing comprehensive and verifiable information.
For example, a blockchain-based system could verify the origin of coffee beans, confirming fair trade practices and sustainable farming methods.
Comparison of Traditional and Blockchain-Based Systems
| Feature | Traditional Supply Chain Tracking | Blockchain-Based Supply Chain Tracking |
|---|---|---|
| Data Management | Information stored in separate databases, potentially leading to inconsistencies and data silos. | All data is stored in a shared, immutable ledger, ensuring accuracy and transparency. |
| Data Access | Limited access to data, often restricted to authorized parties. | All authorized parties have access to the same, real-time information. |
| Security | Vulnerable to data breaches and tampering, potentially leading to fraud and inconsistencies. | Data is secured using cryptographic hashing and distributed ledger technology, making it tamper-proof and highly secure. |
| Transparency | Limited transparency, with information often scattered and difficult to trace. | High transparency, providing a complete audit trail of the product’s journey. |
| Efficiency | Manual processes, potential delays, and errors in data transfer. | Automation of processes through smart contracts, leading to increased efficiency and reduced delays. |
Improving Security and Trust

Blockchain technology significantly enhances the security and trust within supply chains. By leveraging cryptographic principles and immutable data structures, blockchain creates a transparent and auditable record of every transaction, minimizing the risk of fraud and counterfeiting. This heightened security fosters greater trust among stakeholders, from producers to consumers.Blockchain’s inherent security features make it a powerful tool for combating issues like product tampering and intellectual property theft.
The ability to track goods from origin to destination in a secure and transparent manner allows for swift identification of discrepancies and holds actors accountable. This fosters trust and confidence throughout the supply chain.
Cryptography’s Role in Securing Blockchain Data
Cryptography plays a crucial role in safeguarding data on a blockchain. Cryptographic hashing algorithms create unique fingerprints for each block of data, ensuring its integrity. These fingerprints are linked across blocks, forming a chain that’s virtually impossible to tamper with. Advanced encryption methods, such as elliptic curve cryptography (ECC), further enhance security by protecting sensitive information during transactions.
This complex cryptographic structure ensures the authenticity and integrity of the data within the blockchain.
Benefits of Immutability and Tamper-Proof Records
Immutability, a core characteristic of blockchain, ensures that once a transaction is recorded, it cannot be altered or deleted. This tamper-proof nature is invaluable in supply chains. A record of the product’s journey, from raw material to consumer, becomes a verifiable audit trail. This immutability significantly reduces the potential for fraud and counterfeiting. For example, tracing the provenance of luxury goods, like designer handbags, becomes transparent and trustworthy, ensuring consumers receive genuine products.
This also minimizes the risk of fraudulent claims and enhances brand reputation.
Securing Blockchain-Based Supply Chain Data
Protecting blockchain-based supply chain data from unauthorized access requires a multi-layered approach. Strong access controls, combined with robust authentication protocols, are essential. Key management is paramount; only authorized entities should have access to the private keys associated with blockchain accounts. Furthermore, regular security audits and vulnerability assessments can help identify and mitigate potential threats. Implementing multi-factor authentication (MFA) adds another layer of security, ensuring only legitimate users can access the sensitive data.
This stringent approach to access control is crucial to protect the integrity and confidentiality of the data stored on the blockchain.
Streamlining Processes and Efficiency: Blockchain In Supply Chains
Blockchain technology, when integrated into supply chains, significantly streamlines operations and enhances efficiency. By automating key processes and reducing reliance on manual interventions, blockchain fosters faster, more accurate data exchange and order fulfillment, leading to considerable cost savings and improved customer satisfaction.
Automation of Supply Chain Processes
Blockchain’s decentralized and immutable nature enables automation of various stages within a supply chain. Smart contracts, self-executing agreements with predefined conditions, automate tasks like payment processing, inventory management, and order tracking. These automated processes minimize human error, reduce delays, and ensure timely execution of tasks, leading to improved overall efficiency.
Impact of Reduced Paperwork and Manual Intervention
The reduction in paperwork and manual intervention is a substantial benefit of blockchain implementation. Traditional supply chains often rely on numerous documents, each requiring manual handling, verification, and storage. Blockchain eliminates this cumbersome process by recording all transactions on a shared, immutable ledger. This streamlined approach significantly reduces administrative overhead and associated costs, freeing up resources for other critical functions.
Furthermore, reduced manual intervention minimizes the risk of errors, ensuring data accuracy and consistency throughout the supply chain.
Faster and More Accurate Data Exchange
Blockchain facilitates faster and more accurate data exchange by providing a single, transparent source of truth. All participants in the supply chain can access and verify the same information, eliminating the need for multiple data verification steps and reducing delays associated with information transfer. This real-time access to accurate data allows for improved decision-making at each stage of the supply chain, optimizing resource allocation and reducing risks.
A real-world example is a pharmaceutical company using blockchain to track the movement of medications from the manufacturer to the retailer, ensuring transparency and accuracy at every step.
Expedited Order Fulfillment and Delivery
Blockchain’s ability to automate processes and facilitate seamless data exchange significantly expedites order fulfillment and delivery. By providing real-time visibility into inventory levels, order status, and shipment locations, stakeholders can track orders more efficiently, reducing delays and improving customer satisfaction. This streamlined process also allows for better forecasting and proactive management of potential disruptions, enabling companies to respond quickly to unexpected situations and minimize potential losses.
Blockchain technology is revolutionizing supply chains, enhancing transparency and traceability. This integration often relies on robust systems like CRM and ERP systems explained, which are crucial for managing relationships and data across the entire supply chain. Ultimately, blockchain’s impact on supply chains is undeniable, streamlining operations and boosting efficiency.
For example, a retailer using blockchain can track inventory in real time, ensuring timely replenishment and minimizing stockouts.
Cost Reduction and Optimization
Blockchain technology presents significant opportunities for cost reduction and optimization across supply chains. By streamlining processes, enhancing transparency, and minimizing errors, blockchain can translate into substantial financial benefits for businesses. This section will detail the potential cost savings, the impact on fraud and errors, and the improved inventory management enabled by blockchain.
Potential Cost Savings
Implementing blockchain technology in supply chains offers a range of potential cost savings. These savings stem from reduced administrative overhead, fewer errors in documentation, and increased efficiency in inventory management. For example, the elimination of manual paperwork and reconciliation processes can free up valuable human resources for more strategic tasks.
Fraud and Error Reduction
Blockchain’s immutable ledger significantly reduces the risk of fraud and errors. This inherent characteristic of blockchain technology prevents tampering with records and ensures the accuracy of information throughout the supply chain. In a traditional supply chain, discrepancies in documentation, often caused by human error, are common and can lead to significant losses. Blockchain eliminates this vulnerability by creating a transparent and verifiable record of every transaction.
Reduced Operational Costs
Blockchain can significantly reduce operational costs by automating processes and improving efficiency. Automated tracking and verification of goods eliminate the need for multiple intermediaries, reducing administrative burdens and associated costs. Real-time visibility into inventory levels and product movements allows for optimized resource allocation and reduces the risk of stockouts or overstocking, thereby minimizing storage and carrying costs.
Improved Inventory Management
Blockchain’s ability to track inventory in real-time enables businesses to optimize their inventory management strategies. This capability enables businesses to anticipate demand, minimize storage costs, and prevent stockouts. Accurate and timely inventory data facilitates better forecasting, enabling businesses to proactively adjust to market changes and optimize resource allocation.
Comparison of Costs: Traditional vs. Blockchain-Based Supply Chains
A comparison between traditional and blockchain-based supply chains reveals significant cost differences. Traditional supply chains often suffer from high administrative costs due to manual processes, errors in documentation, and delays in verification. These inefficiencies result in increased operational costs and losses due to fraud. Blockchain-based systems, on the other hand, offer a more streamlined approach, leading to reduced costs through automation, transparency, and enhanced security.
This is evident in examples where businesses have successfully reduced operational costs by X% through blockchain implementation. Furthermore, the reduced fraud and error rates translate to significant savings in recovery costs and dispute resolution.
Blockchain’s application in supply chains is becoming increasingly relevant. It’s transforming how goods move through the system, from origin to consumer. This innovative technology ties into broader financial technology (fintech) trends, such as the development of new payment systems and transparent tracking mechanisms, which ultimately enhances the efficiency and security of supply chains. This integration is a key component of blockchain’s future in the industry.
financial technology (fintech) trends are influencing the evolution of blockchain solutions in supply chain management.
Data Integrity and Management
Blockchain’s inherent properties make it a powerful tool for maintaining data integrity and accuracy in supply chains. By leveraging cryptography and distributed ledger technology, blockchain ensures that data modifications are auditable and tamper-proof, significantly enhancing trust and transparency. This secure framework minimizes errors and fraud, creating a more reliable and efficient system.Cryptographic hashing plays a crucial role in maintaining data integrity.
Each block in the blockchain contains a hash, a unique digital fingerprint of the data within. Any alteration to the data would change the hash, instantly flagging the modification. This inherent immutability, coupled with the distributed nature of the ledger, makes tampering virtually impossible.
Cryptographic Hashing for Data Integrity
Cryptographic hashing algorithms, such as SHA-256, generate a fixed-size hash value from variable-length input data. This hash acts as a unique digital fingerprint for the data. If any part of the data changes, the resulting hash will be different. This fundamental characteristic is crucial for verifying data integrity in blockchain-based supply chains. The immutability of the blockchain ensures that any change to the data is recorded and traceable, providing a verifiable history of all transactions and updates.
Data Validation Processes in Blockchain-Based Supply Chains
Data validation processes in blockchain-based supply chains are integral to ensuring the accuracy and integrity of information. These processes typically involve automated checks against predefined rules and standards. For instance, data from various sources (e.g., sensors, documents) is validated against pre-agreed specifications to confirm authenticity and accuracy.
Example Data Validation Processes
- Product Origin Verification: Data from origination points (e.g., farms, factories) is validated against known specifications. This might involve verifying that the product meets certain quality standards and adheres to regulations, ensuring its authenticity. This process might check for the correct certifications or licensing data associated with the product.
- Inventory Management: The system tracks goods throughout the supply chain, ensuring that quantities and locations are consistent across different stages. Data validation ensures that reported quantities align with physical inventory counts at each point in the chain.
- Compliance and Regulatory Checks: Data is validated against compliance standards (e.g., food safety, environmental regulations) at each stage. This verification ensures that the goods adhere to all applicable laws and regulations throughout their journey. This could include checking for permitted chemical residues in food products.
Data Validation Procedures Across Supply Chain Stages
The table below Artikels data validation procedures across different stages of a supply chain. These procedures ensure the accuracy and consistency of data at each point in the chain, enhancing the overall integrity of the supply chain.
| Supply Chain Stage | Data Validation Procedure |
|---|---|
| Origination | Verification of product origin, adherence to quality standards, and compliance with regulations. |
| Manufacturing | Validation of production processes, materials used, and adherence to quality control procedures. |
| Distribution | Tracking and verification of goods in transit, ensuring accuracy in shipment and delivery records. |
| Retail/Consumer | Validation of product authenticity, expiration dates, and compliance with labeling requirements. |
Challenges and Limitations of Blockchain in Supply Chains
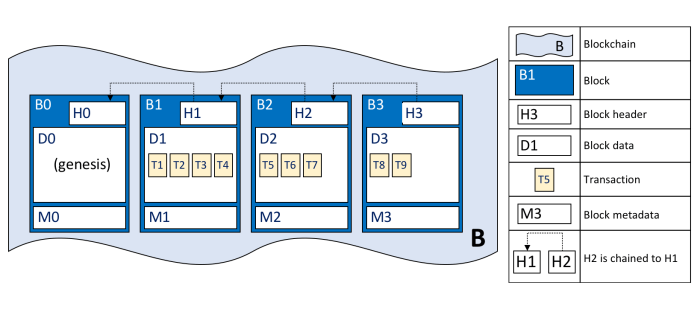
Blockchain technology, while promising, faces hurdles in its application across diverse supply chains. Implementing blockchain solutions requires careful consideration of various factors, ranging from the technical complexities of the technology itself to the practical challenges of integrating it into existing systems. Understanding these challenges is crucial for successful adoption and maximizing the benefits of blockchain in supply chain management.
Scalability and Interoperability Issues
Supply chains often involve a large number of transactions and participants, creating significant demands on the blockchain’s processing capabilities. Traditional blockchain systems, particularly those using proof-of-work consensus mechanisms, can struggle to handle high transaction volumes, potentially leading to delays and bottlenecks. This scalability limitation can be a major deterrent for widespread adoption, particularly in high-volume industries. Interoperability issues also arise when different blockchain platforms or systems are not compatible.
Data exchange and seamless integration across various supply chain partners become challenging when these systems lack common standards. This lack of interoperability can create significant hurdles in data sharing and collaboration.
Complexity of Implementation Across Diverse Supply Chain Partners
Implementing blockchain across a complex supply chain network requires significant effort and coordination among various stakeholders. Different companies often use distinct IT systems and processes, which can create incompatibility issues. Ensuring data consistency and compatibility across various systems is crucial. Gaining buy-in and collaboration from all parties involved is also essential. Different companies may have varying levels of technical expertise and resources, making the implementation process more intricate.
This requires meticulous planning, comprehensive training, and a shared understanding of the blockchain’s potential and limitations among all partners.
Security Risks and Vulnerabilities
Blockchain systems, despite their inherent security features, are not impervious to risks. Smart contracts, which automate transactions, can contain vulnerabilities that, if exploited, can lead to significant financial losses and reputational damage. These vulnerabilities can arise from coding errors, malicious actors, or unexpected events. Compromised private keys or unauthorized access to the blockchain network can compromise the integrity and security of the entire system.
Regular security audits and vulnerability assessments are crucial to mitigate these risks. Furthermore, the decentralized nature of blockchain can sometimes make it harder to trace and identify the source of security breaches.
Future Trends and Developments
Blockchain technology is rapidly evolving, and its applications in supply chains are poised for significant growth. This evolution is driven by the need for enhanced transparency, security, and efficiency in complex global supply networks. The integration of emerging technologies like artificial intelligence (AI) and the Internet of Things (IoT) promises to further revolutionize the sector.The future of blockchain in supply chains hinges on the successful integration of these advanced technologies.
This integration will create a more interconnected and dynamic ecosystem, leading to increased automation and streamlined processes. This, in turn, will result in improved traceability, reduced costs, and increased trust among stakeholders.
Emerging Trends in Blockchain Technology
Blockchain technology continues to evolve, with new protocols and applications emerging. This evolution focuses on enhanced scalability, improved security, and reduced transaction costs. These developments will lead to wider adoption in supply chain management.
Potential Applications of AI and Machine Learning
AI and machine learning offer powerful tools to enhance blockchain’s capabilities in supply chains. These technologies can analyze vast amounts of data from blockchain transactions and IoT devices, enabling predictive modeling and proactive risk management. This data-driven approach can improve inventory management, optimize logistics, and prevent fraud. For instance, AI algorithms can predict potential disruptions in the supply chain, allowing companies to take proactive measures to mitigate these risks.
Integration of IoT Devices with Blockchain
The integration of IoT devices with blockchain allows for real-time tracking and verification of goods throughout the supply chain. This integration provides an immutable record of each stage of the process, from origin to delivery. This data is crucial for monitoring product quality, identifying potential issues, and ensuring product authenticity. Imagine a refrigerator in a warehouse equipped with sensors, tracking the temperature and humidity.
This data can be recorded on a blockchain, ensuring that the product meets quality standards.
Forecast of Future Growth and Impact
Blockchain technology is expected to continue its growth trajectory in supply chains. Its increasing adoption will be fueled by the demonstrable benefits it offers in terms of transparency, security, and efficiency. Major industries, such as food and pharmaceutical supply chains, are already exploring the use of blockchain to improve traceability and safety. This adoption will result in a more robust and resilient supply chain network.
For example, the adoption of blockchain in the food industry is already helping to reduce foodborne illnesses by enabling better tracking and tracing of products, ensuring consumers have access to verified information about the origin and handling of their food. This level of transparency and trust will become increasingly important as global supply chains become more complex.
Case Studies and Real-World Examples
Blockchain technology is rapidly gaining traction in supply chains, and numerous companies are adopting it to enhance transparency, traceability, and security. Real-world implementations offer valuable insights into the potential and challenges of blockchain in this context. These case studies demonstrate the varying degrees of success and highlight areas where improvements are still needed.
Food and Beverage Industry
Implementing blockchain in the food and beverage sector offers a powerful solution for addressing food safety and authenticity concerns. Companies can track products from origin to consumer, verifying the entire supply chain.
- A multinational food corporation successfully implemented a blockchain solution to enhance the traceability of its beef supply chain. By recording every step from farm to processing plant to retail, the company improved food safety and consumer trust. The system provided detailed information on each animal’s journey, including origin, handling, and processing dates. This facilitated quicker and more targeted responses to any potential food safety issues.
The result was a demonstrably improved reputation for food safety and quality.
- A major wine producer utilized blockchain to verify the authenticity and origin of their wine. This involved recording vineyard location, vintage, and processing details. The solution ensured consumers received genuine products, thus bolstering the brand’s reputation and enhancing consumer confidence. It also facilitated faster identification and removal of counterfeit products.
Pharmaceutical Industry
The pharmaceutical industry is particularly susceptible to counterfeiting, and blockchain can play a critical role in maintaining product integrity and safety. Tracking medication throughout the supply chain, from manufacturing to distribution, provides significant advantages.
- A pharmaceutical company used blockchain to record the complete history of a batch of medication. This included information on manufacturing, storage, and distribution. The system offered unparalleled visibility and traceability, aiding in the identification and resolution of any supply chain issues, ultimately safeguarding patients and maintaining product integrity.
- A pharmaceutical distributor implemented a blockchain solution to track prescription drugs, verifying their authenticity and ensuring compliance with regulations. The enhanced transparency and security measures helped to prevent the distribution of counterfeit medication.
Automotive Industry
The automotive industry, with its complex supply chains, can benefit from blockchain’s ability to enhance transparency and efficiency. Tracking parts and vehicles across various stages of production and distribution is made more straightforward.
- A major automotive manufacturer used blockchain to track the provenance of critical components in their vehicles. This provided comprehensive visibility into the supply chain, which improved the identification of potential issues and facilitated faster response times.
Comparison of Blockchain Implementations, Blockchain in supply chains
| Industry | Specific Benefits | Challenges |
|---|---|---|
| Food and Beverage | Enhanced traceability, improved food safety, increased consumer trust, faster response to issues | Integration with existing systems, scalability, cost of implementation, and workforce training. |
| Pharmaceutical | Preventing counterfeiting, ensuring product integrity, enhanced security, compliance with regulations | Data privacy concerns, regulatory hurdles, and potential resistance to change from established practices. |
| Automotive | Improved supply chain transparency, efficient tracking of components, reduced fraud | Complex integration with existing systems, potential need for standardization across the supply chain, and regulatory compliance. |
Epilogue
In conclusion, blockchain technology presents a paradigm shift in supply chain management, offering a compelling solution for increased transparency, security, and efficiency. While challenges remain, the future of supply chains is likely to be heavily influenced by blockchain’s ability to streamline processes, optimize costs, and enhance trust. Companies that adopt this technology early will gain a significant competitive advantage in the years to come.
Key Questions Answered
What are some common security risks associated with blockchain in supply chains?
While blockchain is inherently secure, potential vulnerabilities exist if not implemented correctly. These include single points of failure in the network, the need for robust access controls, and the risk of sophisticated attacks targeting the blockchain’s infrastructure or individual participants.
How does blockchain enhance traceability in supply chains?
Blockchain provides a permanent and immutable record of every transaction and movement of goods throughout the supply chain. This creates a complete audit trail, allowing for easy tracking of products and identifying potential issues or bottlenecks.
What are the scalability limitations of blockchain technology in supply chains?
Some blockchain platforms can struggle to handle the high volume of transactions in large-scale supply chains. This issue is being addressed through advancements in scaling solutions, but it remains a consideration for large enterprises.
How does blockchain reduce fraud in supply chains?
The immutable nature of blockchain records makes it very difficult to alter or manipulate data, significantly reducing the opportunity for fraud. This transparency and verifiable information reduces instances of counterfeiting, misreporting, and other fraudulent activities.